Can fiber optic patch cords be used to connect servers?
2025-07-21
Fiber optic patch cords can be directly connected to servers, but specific conditions must be met and operational risks must be taken into account. The core points are as follows:
1. Physical interface compatibility
Applicable scenarios:
The server is equipped with fiber optic network cards (such as SFP+, QSFP28 ports), and the patch cord connectors are physically compatible with the network card ports (e.g. LC-LC patch cord plugs into SFP ports).
Short distance temporary debugging (such as firmware upgrade, diagnosis), or point-to-point direct connection to two servers (requiring cross mode).
Disable scenario:
The server only has an electrical port (RJ45) and uses a fiber optic adapter module (requires additional power supply and configuration).
Multi mode patch cords (OM3/OM4) forcibly connect to single-mode network cards (with the risk of optical signal damage).
2. Connecting risks and protection
Link stability issue:
When directly connected to a non relay device, bending/stretching of patch cord wires can easily cause a significant increase in light attenuation, triggering a server network card alarm (logging RX power low).
When the armored patch cord is not used, stepping on it or squeezing the cabinet door may break the fiber core.
Mandatory requirements for electrostatic protection:
Before plugging or unplugging, an anti-static wristband must be worn and grounded. The server network card photoelectric module is sensitive to static electricity (ESD damage is irreversible).
Prohibit hot plugging: It is necessary to shut down and turn off the power before operation (although some enterprise level servers support hot plugging, manufacturers still recommend turning off the power).
3. Priority of alternative operation and maintenance solutions
Recommended standard practice:
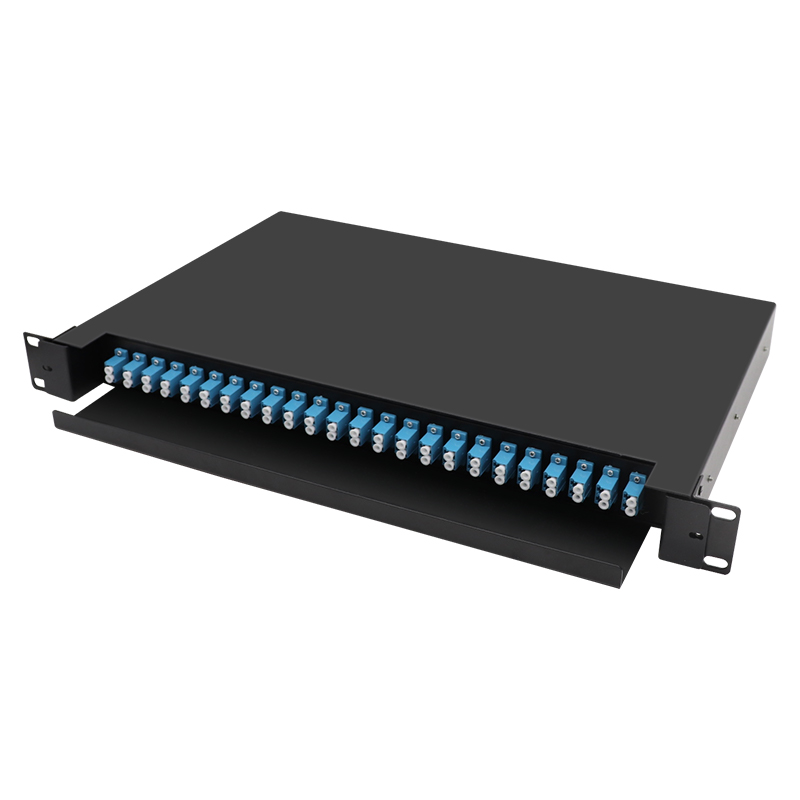
Through fiber optic distribution frame transfer: one end of the patch cord is connected to the server, the other end is connected to the distribution frame port, and then connected to the switch through the backbone fiber optic cable (reducing equipment direct connection losses).
Dual link redundancy for important business servers: Two patch cords are connected to two independent switches respectively to avoid single point failures.
Direct connection only for temporary scenarios:
Equipment troubleshooting period (such as temporarily connecting the service cluster when the switch is down).
Initial inspection of new server deployment (basic connectivity test before connecting to the official network).
cooperate with PUXIN?
Contact us to find out how our products can transform your business and
take it to the next level.