Shielded or unshielded keystone jacks? When to think of protection from EMI?
2025-12-01
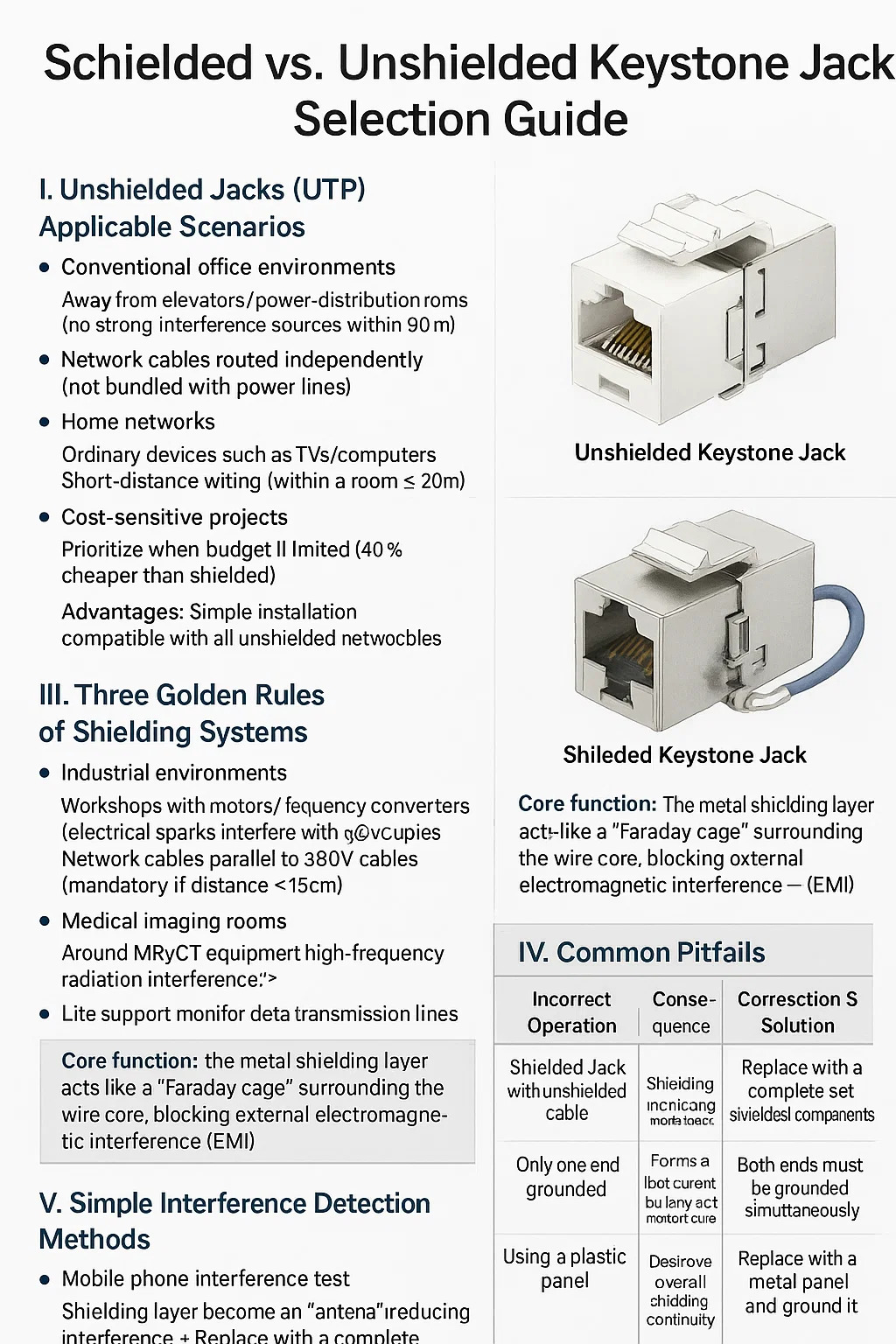
Shielded vs. Unshielded Keystone Jack Selection Guide
Content
I. Unshielded Jacks (UTP) Applicable Scenarios
● Conventional office environments
Away from elevators/power distribution rooms (no strong interference sources within 30 meters)
Network cables are routed independently (not bundled with power lines)
● Home networks
Ordinary devices such as TVs/computers
Short-distance wiring (within a room ≤ 20 meters)
● Cost-sensitive projects
Prioritize when budget is limited (40% cheaper than shielded)
Advantages: Simple installation, compatible with all unshielded network cables
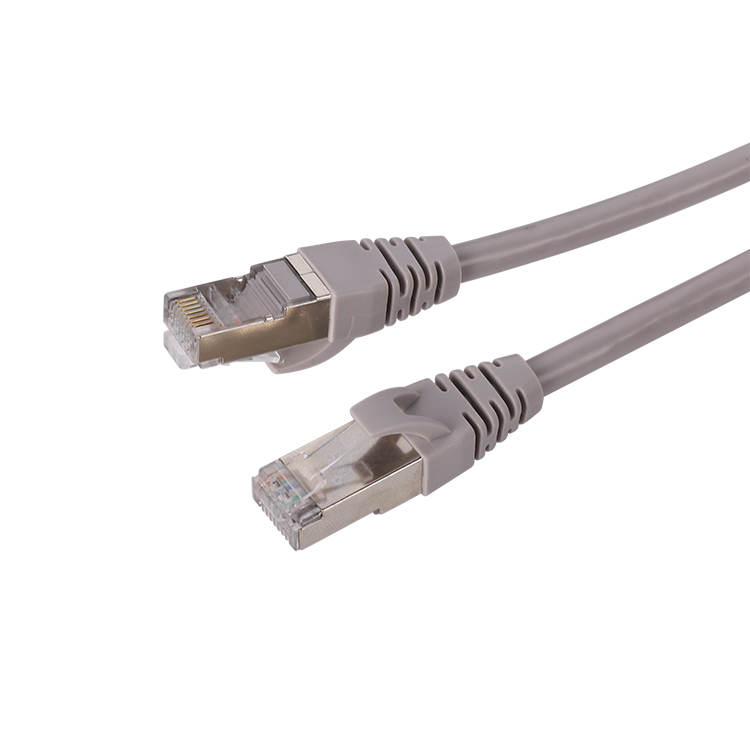
II. Scenarios Where Shielded Jacks (STP/FTP) are Required
● Industrial environments
Workshops with motors/frequency converters (electrical sparks interfere with network signals)
Network cables parallel to 380V cables (mandatory if distance < 15cm)
● Medical imaging rooms
Around MRI/CT equipment (high-frequency radiation interference)
Life support monitor data transmission lines
● High-risk outdoor areas
Near base station antennas (electromagnetic interference)
Areas prone to thunderstorms (shielding layer can guide induced lightning)
Core function:
The metal shielding layer acts like a "Faraday cage" surrounding the wire core, blocking external electromagnetic interference (EMI)
III. Three Golden Rules of Shielding Systems
● Full shielding:
Network cable + Keystone Jack + RJ45 connector must all be shielded (failure of any one component renders the system ineffective)
● Dual-end grounding:
Grounding the patch panel at the cabinet end
Grounding the switch metal casing at the equipment end
● Anti-oxidation maintenance:
Grounding contacts should be sanded every six months (to prevent rust from causing grounding failure)
IV. Common Pitfalls
| Mistake | Consequence | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Using shielded jacks with UTP cable | Shield acts as an antenna, attracting interference | Replace entire run with STP/FTP cable + shielded components |
| Grounding only one end | Creates ground loops that fry ports | Ground BOTH ends to same point |
| Mounting on plastic wall plates | Breaks shield continuity | Switch to metal-faced panels with grounding tabs |
V. Simple Interference Detection Methods
● Mobile phone interference test:
Hold the phone close to the network cable during a call → If you hear a "buzzing" sound, interference exists
● Multimeter detection method:
Measure the voltage between the network cable and the ground wire > 1V → Grounding needs to be checked
● Practical stress test:
Ping the gateway while the copier is working → If the packet loss rate exceeds 5%, it needs to be blocked.
cooperate with PUXIN?
Contact us to find out how our products can transform your business and
take it to the next level.