What is a fiber optic patch cord?
2025-08-11
Analysis of fiber optic patch cord
1. Basic Definition
Physical form: A prefabricated short distance optical cable consisting of a fiber core (glass/plastic), cladding, and sheath, with fixed connectors (such as LC, SC) at both ends.
Core function: Directly transmit optical signals between devices, replacing traditional copper cables for electrical signal transmission.
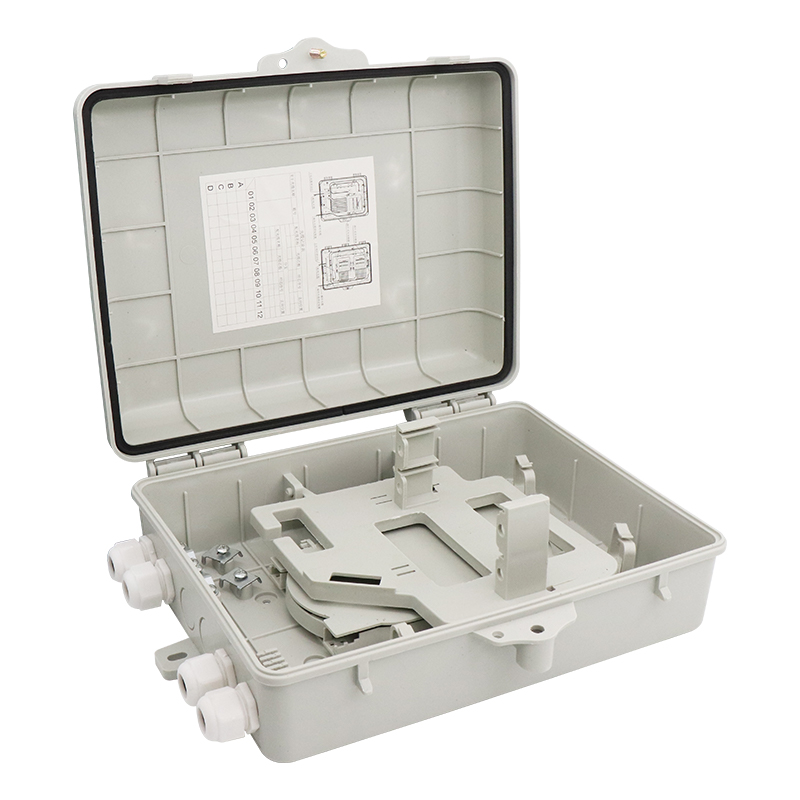
2. Core components
Core type:
Single mode (SMF): thin core (9 µ m), long-distance (10km+), laser source.
Multi mode (MMF): Coarse core (50/62.5 µ m), short distance (≤ 550m), LED light source.
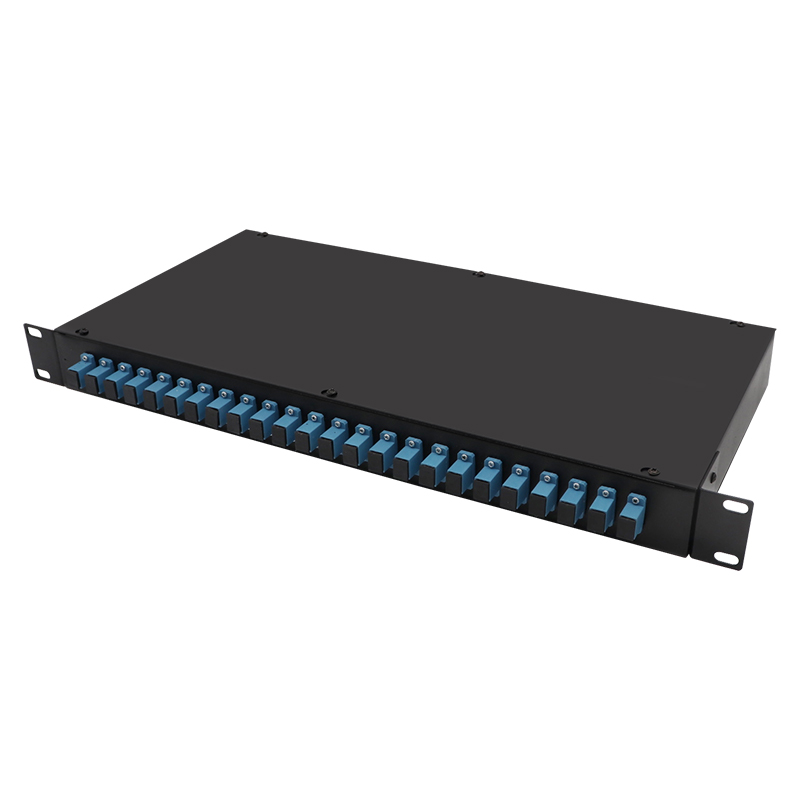
Connector differences:
LC: miniaturization, high density (mainstream in data centers).
SC: Snap on type, commonly used in industrial monitoring.
MPO: Multi core aggregation (40G/100G high-speed scenarios).
3. Typical application scenarios
Device direct connection: point-to-point short-range interconnection between switches servers, optical transceivers cameras, etc.
Distribution frame transfer: As an active link in integrated cabling, it is easy to maintain and replace.
Special environment:
Strong electromagnetic interference zone (substation, radar station).
Explosion proof requirements for places (petrochemical tunnels).
4. Usage restrictions
Irreplaceability:
Responsible only for physical layer signal transmission and does not participate in protocol conversion or signal amplification.
Both ends must be matched with optical modules/fiber optic equipment (additional photoelectric conversion is required for electrical interface equipment).
Lifespan and maintenance:
Bending radius<5cm can easily lead to permanent damage and requires protection against trampling/compression.
Contamination of the connector end face (dust, oil stains) can cause complete signal interruption.
5. Selection key
Distance fixed mode: Short distance multimode (≤ 550m), long-distance single-mode.
Environmental protective sheath:
Indoor PVC, outdoor/armored anti tensile and rodent resistant.
Choose the bending insensitive type (such as IEC 60794-2-50 standard) for repeated bending scenarios.
Compatibility verification:
The connector is physically matched with the device port (LC plug SFP, SC plug GBIC).
The wavelength is consistent with the optical module (850nm multimode/1310nm single-mode).
| Category | Key Details | Critical Notes |
| Definition | Pre-terminated short fiber cables with connectors at both ends | Acts as a plug-and-play optical link between devices |
| Core Types | • Single-mode (SMF): Thin core (9µm), long-distance• Multi-mode (MMF): Thick core (50/62.5µm), short-range | Mode mismatch causes signal failure |
| Connectors | • LC (compact, • LC (compact, high-density)• SC (snap-in, rugged)• MPO (multi-fiber, high-speed) | Connectoriber, high-speed) |
| Typical Uses | • Switch-to-server links• Patch panel cross-connects• EMI-sensitive environments | Not for direct electrical signal conversion |
| Limitations | • Requires compatible optical equipment• No signal processing capability• Fragile if mishandled | Bending <5cm radius causes permanent damage |
| Selection Guide | • Distance: SMF for >550m, MMF for short runs• Environment: Armored for outdoors, bend-insensitive for tight spaces | Always verify connector and wavelength compatibility |
| Do | Don't |
| Use lint-free wipes for cleaning connectors | Never touch exposed ferrules |
| Maintain >5cm bend radius | Don't force mismatched connectors |
| Verify light transmission before use | Avoid coiling near power cables |
| Store unused cables with protective caps | Never hot-plug without verification |
cooperate with PUXIN?
Contact us to find out how our products can transform your business and
take it to the next level.