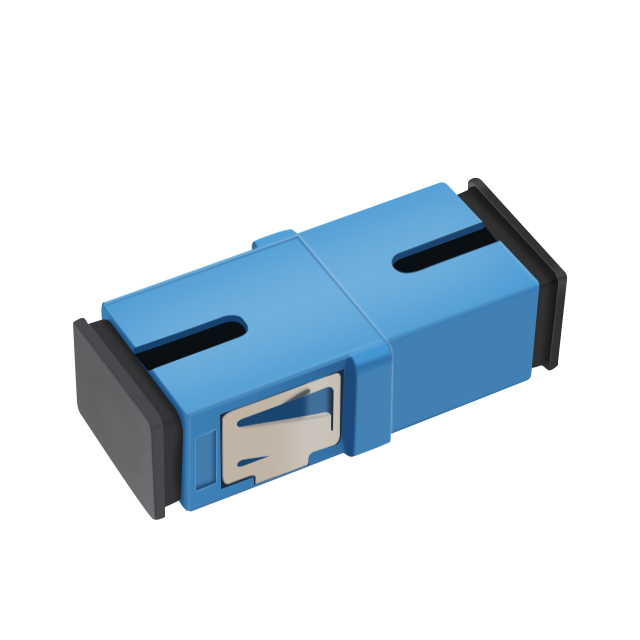
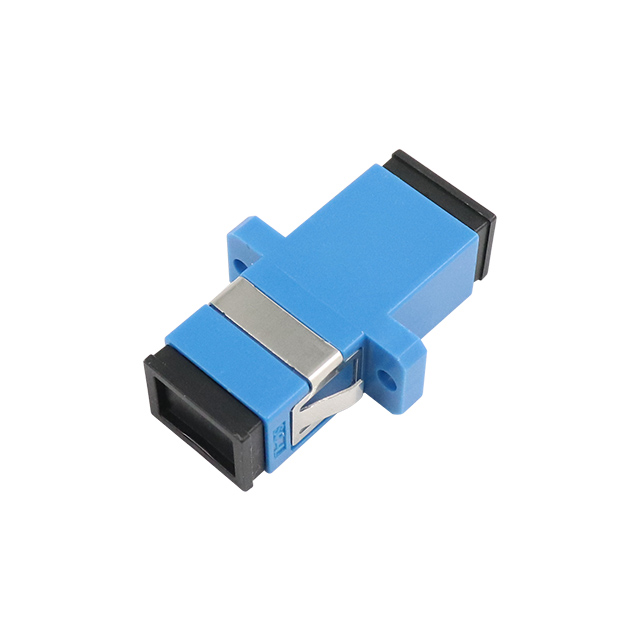
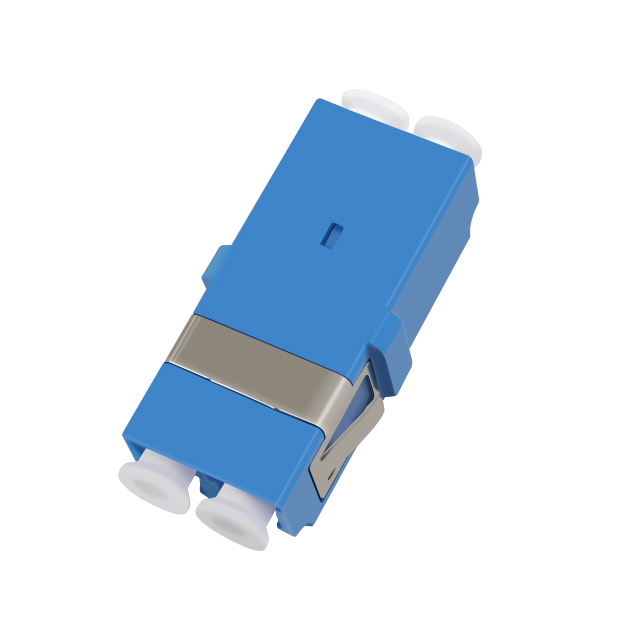
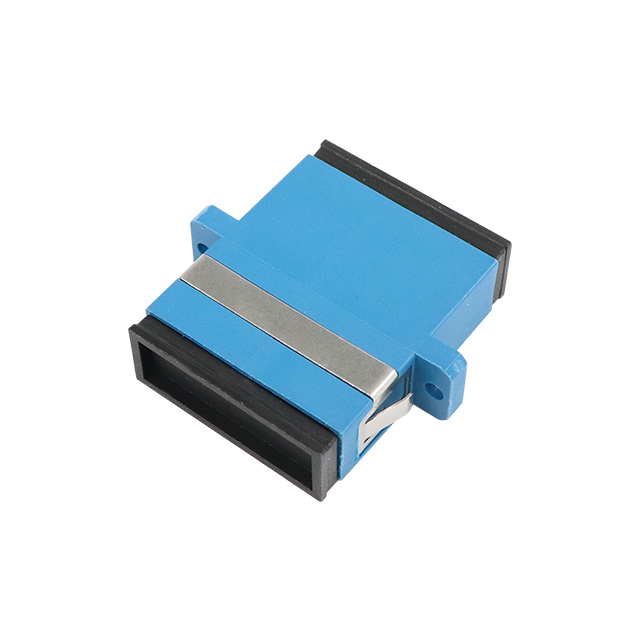
OEM/ODM Fiber Optic Adaptor
Fiber Optic Adaptor Supplier

PUXIN Story
Ningbo Puxin Electronic Technology Co., Ltd has established for more than 15 years, which is specialized in the production of integrated network cabling products and optic fiber products, including copper CAT5E, CAT6, CAT6A, CAT7, CAT8, such as keystone jack, patch panel, RJ45 connector, patch cord, and other related products.
As a China Fiber Optic Adaptor Supplier and OEM/ODM Fiber Optic Adaptor Company , Our company has advanced manufacturing equipment, testing equipment, and scientific and quality control methods. We have rich experience in manufacturing OEM and ODM products. At present, our products have been exported to Southeast Asia, South America, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, and other countries.
We sincerely look forward to working together with domestic and foreign merchants to create common development. Friends from all walks of life are welcome to visit, guide, and negotiate business.

Complete And Stable Supply Chain
Our R&D team has more than 10 years of experience in the production and design industry. We can accept OEM and ODM orders, you only need to provide customized sizes and shapes to enjoy professional customization services.
Create Safer Cabling Connections
PUXIN has an on-site engineering team and a mold manufacturing team equipped with complete production lines including stamping, plating, injection molding, automatic insertion and assembly capabilities to ensure that your products meet the requirements of safety standards for all processes.

The Entire Supply Chain is Third-Party Certified
We insist on using new environmentally friendly raw materials. The finished products must pass ROHS and FLUKE testing before they can be sold. Related products have been certified by well-known institutions in the industry such as CCC, CE and ROHS. certificate and holds multiple product research and development patents.

PUXIN Collaboration System
Our goal is to provide the market and customers with customized solutions, whether it is a single product or a complete set of products.
We will respond patiently and carefully to any inquiries and feedback from customers, and provide professional and reasonable quotations.
For any new products from customers, we will communicate with customers very professionally, listen to their opinions and give useful suggestions to ensure high-quality products.
For any orders from customers, we will complete them on time, quality and quantity.
We take the time and effort to solve every problem, no matter how mundane you may encounter it. We will always accommodate you, and you'll find that we speak your language and understand your technical issues. This is why we have been so successful over the years working with our clients from more than 30 countries.
Latest Updates
Provide you with the latest enterprise and industry news.
Fiber Optic Adaptor Industry Knowledge
Can the fiber optic adapter withstand temperature fluctuations?
Yes, fiber optic adapters are typically designed to withstand a range of temperature fluctuations. They often use special materials and structures to ensure stability and reliability under various environmental conditions. The design of these adapters takes into account the impact that temperature changes may have on their performance, and measures are taken to reduce this impact.
In fiber optic networks, adapters are often used to connect fiber optic cables between different devices or connectors. Therefore, they need to work reliably in a wide range of temperature environments, whether in a constant-temperature environment inside a data center or in an outdoor environment subject to natural temperature fluctuations. Therefore, fiber optic adapters are usually designed to have good temperature adaptability to ensure normal operation in various working environments.
How does the fiber optic adapter transmission rate affect system response time?
The transmission rate of a fiber optic adapter has a significant impact on system response time. System response time refers to the time it takes for a computer system to process a task or request and provide the corresponding result after receiving it. As a key component of data transmission, the fiber optic adapter's transmission rate directly determines the speed of data transmission in the optical fiber, which in turn affects the system response time.
First, a higher transfer rate means that the fiber optic adapter can transfer data faster. When the system receives a request, the adapter can quickly transmit the data from the sending end to the receiving end, reducing the time required for data transmission. This helps the system process tasks faster, thereby improving system response time.
Secondly, the transmission rate of the fiber optic adapter also affects system processing delay and queuing delay. Processing latency refers to the time it takes the processor to execute a task, while queuing latency refers to the time a task waits in a queue for processing. When the transmission rate of the fiber optic adapter is increased, the data transmission speed is accelerated, which reduces the time the processor waits for data, thus reducing the processing delay. At the same time, due to the improvement of data transmission efficiency, the time for tasks waiting for processing in the queue will also be reduced, reducing queuing delay.
In addition, the transmission rate of the fiber optic adapter also affects the utilization of network bandwidth. If the adapter's transfer rate matches or is higher than the network bandwidth, network bandwidth utilization will be improved and data transfer will be smoother, further reducing system response time.
To sum up, the transmission rate of the fiber optic adapter ultimately affects the system response time by affecting many aspects such as data transmission speed, processing delay, queuing delay and network bandwidth utilization. Therefore, when selecting a fiber optic adapter, it is necessary to select an appropriate transmission rate based on the system's response time requirements to ensure that the system can respond to user requests quickly and efficiently.
cooperate with PUXIN?
Contact us to find out how our products can transform your business and
take it to the next level.
Ningbo Puxin Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. is a professional supplier of electrical engineering and integrated wiring product research and development and manufacturing.
-

No.43 of Xiaotuanpu Road, Guanhaiwei Town, Cixi Ningbo City, Zhejiang, China
-
-

8615924366333
-